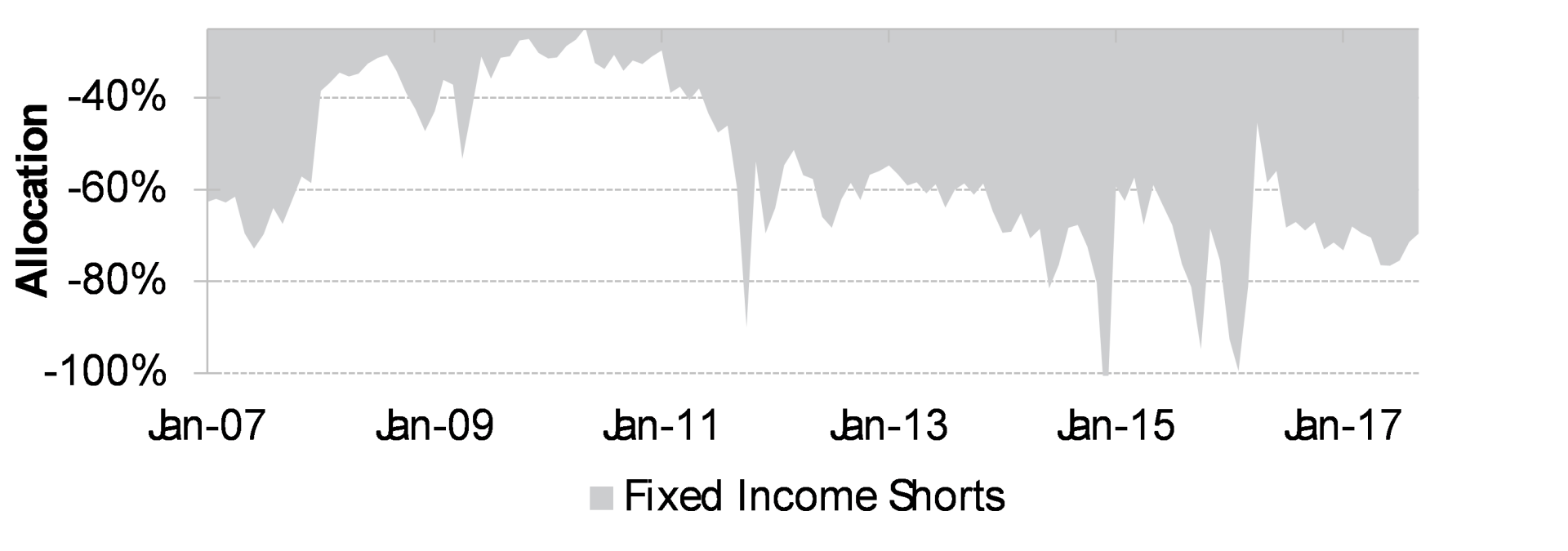Equinox Partners, L.P. - Q3 2017 Letter
Dear Partners and Friends,
PERFORMANCE & PORTFOLIO
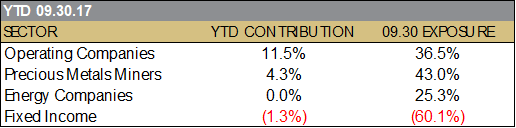
Equinox Partners gained +10.0% in the third quarter of 2017. For the year to date through October 31, we estimate our fund was up +10.8%.[1]
In October, we sold half of our Ferreycorp position; it remains a sizeable holding. We also began shorting U.S. corporate bonds. In the third quarter, we made modest changes to several positions and fully exited Argentina.
portfolio construction
“We seek to own a concentrated portfolio of undervalued, high-quality businesses and sell short overpriced securities that offer an attractive risk/reward while positioning our fund on the right side of financial history.” —Equinox Partners monthly summary
Owning “…a concentrated portfolio of undervalued, high-quality businesses...” and shorting “… overpriced securities that offer an attractive risk/reward…” is a typical hedge fund strategy. And, positioning our fund on “the right side of financial history” is an implicit objective of long-term macro investors. But, marrying these micro and macro objectives in one fund, as we have for the past twenty-three years in Equinox Partners, is unusual.
The resulting portfolio is built to profit from both the financial status quo as well as its inevitable end. Specifically, we expect the undervalued, superior businesses we own to compound their intrinsic value during periods of relative macroeconomic stability. As such, we are conventional better-business value investors. We also believe that positioning our fund on the right side of financial history has never been more important. Herb Stein famously quipped that “if something cannot go on forever, it will stop.” The clearly unsustainable feature of the current macroeconomic environment can be summed up in just three words: too much debt.
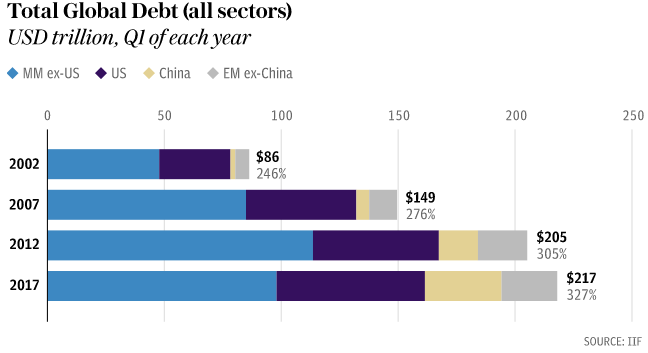
For decades, the developed world has been on a historically unprecedented debt binge, and since 2008 much of the emerging world has joined the party. The result is a world awash in debt of every variety: government debt, central bank-owned debt, personal debt, structured debt, junk debt, shadow-bank debt, etc. Recent debt records include the $247 billion of CLOs issued in the first nine months of 2017,[2] and the year-to-date leveraged loan issuance of $1.25 trillion which eclipsed the previous full-year record set in 2013.[3] To put the current credit binge into perspective, the total amount of global debt today is 45% higher than it was when Lehman Brothers declared bankruptcy a decade ago.[4]
Paradoxically, and contrary to our expectations in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis, more debt has made the world both more stable and more fragile at the same time. Specifically, the world’s growing debt burden has resulted in unprecedented short-term financial stability by encouraging an unprecedented coordination amongst policy makers, especially central bankers. But, there is no free lunch, and this highly-engineered short-term stability has come at an enormous long-term cost. Specifically, stability is being purchased with ever more debt, and ever more debt leads to greater long-term fragility.
With policy makers successfully smothering every whiff of instability with more debt for ten years running, most market participants have been reduced to buying the dips rather than thinking about the long-term implications of this policy. This pattern, combined with sustained deflationary forces, has left few concerned that such high debt levels will prevent central bankers from raising rates to head off future inflation. So long as the market remains unconcerned about this still hypothetical constraint, the actual limit to the amount of debt that a society can support will likely remain remote.
Japan, with government debt to GDP over 250% and total debt to GDP well over 500%, is a case study in financial extremes and extreme complacency.[5] In fact, Japan’s dangerous debt load has not only corresponded with lower yields but also with a growing sense that there may be no upper bound to the amount of debt that a country can support. Emboldened by the market’s indifference to Japan’s financial path, the Abe administration recently walked back its plans to balance the budget by 2020 and added a super-dove to the BOJ board that makes Kuroda look hawkish. With the Japanese 10 year bond still hovering at just over a 0% yield to maturity, Japan is the most extreme example of what now passes for normal in the first world.
Even though today’s surreal combination of short-term stability and ever more debt is often treated as inevitable, it remains unwise in our opinion to make investments that depend on this status quo. Accordingly, we continue to broadly avoid heavily-indebted geographies. Our strategy of debt avoidance is prominently reflected in the country weightings on page two of our monthly fund summary. Our two top country weightings, Peru and the United Arab Emirates, are both notably underleveraged.
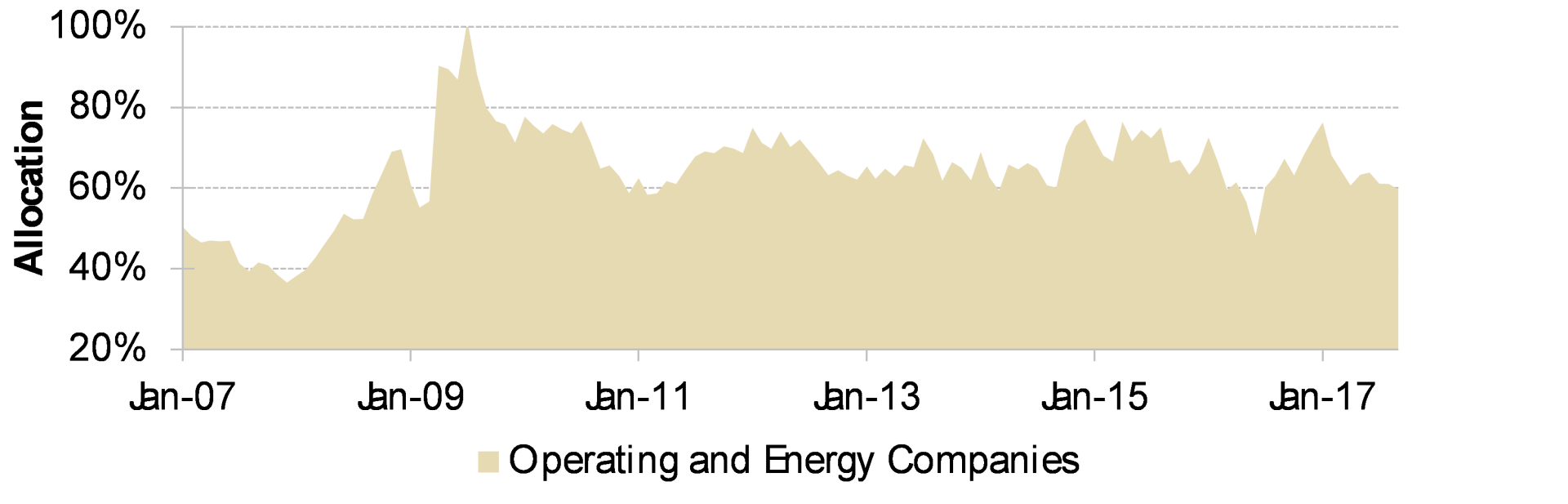
Our Canadian E&P investments are also well positioned to weather the end of the current debt bubble. While it is certainly true that increasing debt encourages consumption which is positive for oil and gas demand, it is equally true that cheap, abundant debt has also been used to develop marginal oil and gas assets. The development of these marginal reserves with easy money has applied an enormous downward pressure on oil and gas prices in recent years. Bill Thomas, the highly-regarded CEO of EOG, recently speculated that as many as half of the producing wells in North America are not sound full-cycle investments at $50 oil. Given the capital intensity of the E&P sector, it is no stretch to see how more disciplined capital markets could lead to higher energy prices. Moreover, our E&P companies, with conservative balance sheets and some of the lowest costs assets, can continue to grow quickly at current energy prices without any outside capital.
Together our emerging market and E&P investments account for 57% of partners’ capital. These investments are intended to prosper during the status quo as well as weather its inevitable end. Specifically, in a credit contraction, we even think these companies could outperform predictable blue chips such as Colgate-Palmolive or Proctor & Gamble. Even conceding that Colgate-Palmolive and Proctor & Gamble’s businesses will plod on in a difficult macroeconomic environment, paying over twenty times forward earnings for low-growth companies is risky. Our operating and energy investments by comparison trade at 11.7x forward earnings and 6.3x forward cash flow, respectively.
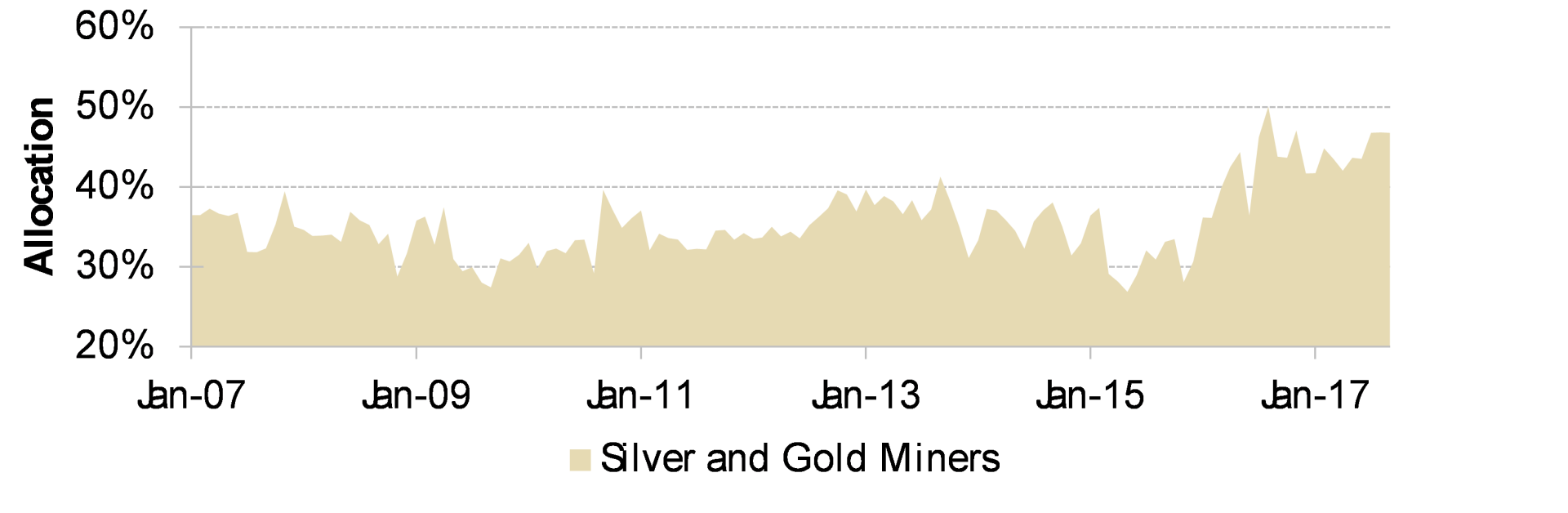
We’ve positioned the other half of our portfolio to capitalize on the world’s over-indebtedness rather than just manage through it. Our long investments in gold and silver mining and short positions in low yielding bonds are a reflection of our confidence that central banks will choose to preserve short-term stability rather than purchasing power if forced to decide between the two. We believe this preference, while seemingly irrelevant during times of stability, will become obvious during times of financial instability.
With respect to gold and silver, so long as the bias for stability and the low rates necessary to sustain it persist, monetary metals will remain attractive alternatives to first world money. Both gold and silver have appreciated substantially so far this century, a trend that we believe will continue until the problem of over-indebtedness is eventually resolved. Accordingly, as gold and silver miners declined post 2011, we have increased our position, making this our single largest sector weighting at 43%. Our portfolio of miners are attractive investments in a sideways metals price environment and are poised to perform exceptionally well when gold and silver prices rise.
With respect to our bond shorts, today’s combination of debt and rates has created a catch-22 for policy makers. If rates go up society cannot pay its debts. But, if rates don’t go up, society lacks the political will to reign in its debts. This dynamic has created an insoluble problem from a policy perspective and an attractive opportunity for short sellers. And, while rates have gone lower than we thought they would, shorting today’s low yielding debt is more attractive than it has ever been. We are accordingly increasing our fixed income short exposure.
There are, of course, a myriad of other ways that we could position our fund for the end of the great debt bubble. Cryptocurrencies, for example, have been top of mind for many investors. But, to be blunt, at this point, with Bitcoin up over 500x in 5 years, cryptocurrencies appear to be more a part of the problem than the solution. While unbacked digital money has been an excellent trade, it has also been a beneficiary of today’s liquidity driven bubble rather than being opposed to it.
Conclusion
With the humility that comes from having been wrong about macro outcomes for years, we believe that the end of the world’s enormous debt bubble is close at hand. The U.S. federal government is poised to embark upon a fiscal expansion on the back of eight years of economic expansion while the economy is at full employment. Specifically, the federal government is poised to increases its fiscal deficit by hundreds of billions of dollars as commodity prices and wage rates are showing new signs of life.[6] Perhaps the evil of inflation has been so permanently slayed that such factors no longer matter, but we seriously doubt it.
Sincerely,
Sean Fieler Daniel Gittes
END NOTES
[1] Sector exposures calculated as a percentage of 9.30.17 pre-redemption AUM. Performance contribution in US dollars, gross of fees and fund expenses. Interest rate swaps notional value and P&L included in Fixed Income. P&L on cash and short proceeds and market value exposures for derivatives excluded. Unless otherwise noted, all company-specific data derived from internal analysis, company presentations, or Bloomberg.
[2] Whittall, Christopher, The Wall Street Journal, 10.22.17. Hunt for Yield Fuels Boom in Another Complex, Risky Security
[3] Rennison, Joe and Platt, Eric, Financial Times, 10.29.17. Wall St banks ride boom in leveraged loans as volumes soar
[4] Evans-Pritchard, Ambrose, The Telegraph, 06.28.17. Janet Yellen Courts Fate by Trumpeting End to Financial Crises
[5] Trading Economics, source Japanese Ministry of Finance; Pimco, Seven Salient Left Tail Scenarios
[6] Bureau of Labor Statistics, Employment Cost Index-September 2017.
Release October 31, 2017.